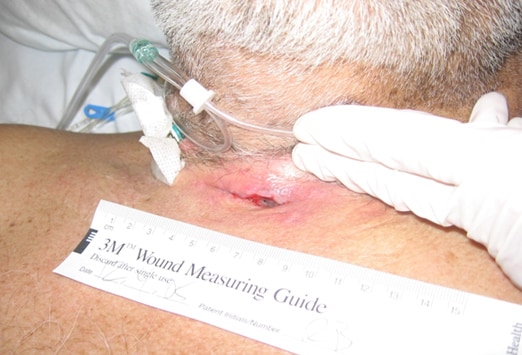
Complications to watch out for:
Infections
Tracheomalacia- Tracheomalacia is the breakdown of the natural rigid
structure of the trachea that leads to a flaccid airway Skin breakdown
NCLEX PROBLEMS You need to know how to solve:
Dislodgement of the tracheal tube during the first postoperative week is considered a medical
emergency; therefore, tube security is a priority.

1. hemorrhage- A small amount of bleeding is expected after the initial procedure and after every tracheostomy tube change. This small amount of bleeding is normally self-limited. If bleeding is more than minimal or if it continues, the surgeon should be contacted.

2. 2. tube dislodgement- (If stoma new and is less than a week old) Immediate treatment in complete decannulation includes mask ventilation and then orotracheal intubation
(If stoma is older than a week) If the problem is discovered quickly, the tube can usually
be easily replaced.
3. 3. loss of airway- SAME AS TUBE DISLODGEMENT

4. 4. tube obstruction- The 1ST step in caring for a tracheostomy patient in respiratory distress is to remove and inspect the inner cannula. If the cannula is clogged with secretions, it can be quickly cleaned and/or replaced with a new one. If the patient remains in distress, the nurse should immediately call for help and then attempt to insert a suction catheter. Easy passage of the suction catheter with return of tracheal secretions confirms that the tube is in proper position. If you feel resistance or can only get the suction catheter a few inches in then you may be in a false passage.
No comments:
Post a Comment